publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order. generated by jekyll-scholar.
2025
-
 Q-restore: quantum-driven framework for resilient and equitable transportation network restorationDaniel Udekwe , Ruimin Ke , Jiaqing Lu , and 1 more authorarXiv preprint arXiv:2501.11197, 2025
Q-restore: quantum-driven framework for resilient and equitable transportation network restorationDaniel Udekwe , Ruimin Ke , Jiaqing Lu , and 1 more authorarXiv preprint arXiv:2501.11197, 2025Efficient and socially equitable restoration of transportation networks post disasters is crucial for community resilience and access to essential services. The ability to rapidly recover critical infrastructure can significantly mitigate the impacts of disasters, particularly in underserved communities where prolonged isolation exacerbates vulnerabilities. Traditional restoration methods prioritize functionality over computational efficiency and equity, leaving low-income communities at a disadvantage during recovery. To address this gap, this research introduces a novel framework that combines quantum computing technology with an equity-focused approach to network restoration. Optimization of road link recovery within budget constraints is achieved by leveraging D Wave’s hybrid quantum solver, which targets the connectivity needs of low, average, and high income communities. This framework combines computational speed with equity, ensuring priority support for underserved populations. Findings demonstrate that this hybrid quantum solver achieves near instantaneous computation times of approximately 8.7 seconds across various budget scenarios, significantly outperforming the widely used genetic algorithm. It offers targeted restoration by first aiding low-income communities and expanding aid as budgets increase, aligning with equity goals. This work showcases quantum computing’s potential in disaster recovery planning, providing a rapid and equitable solution that elevates urban resilience and social sustainability by aiding vulnerable populations in disasters.
@article{udekwe2025q, title = {Q-restore: quantum-driven framework for resilient and equitable transportation network restoration}, author = {Udekwe, Daniel and Ke, Ruimin and Lu, Jiaqing and Guo, Qian-wen}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.11197}, year = {2025}, dimensions = {true}, } -
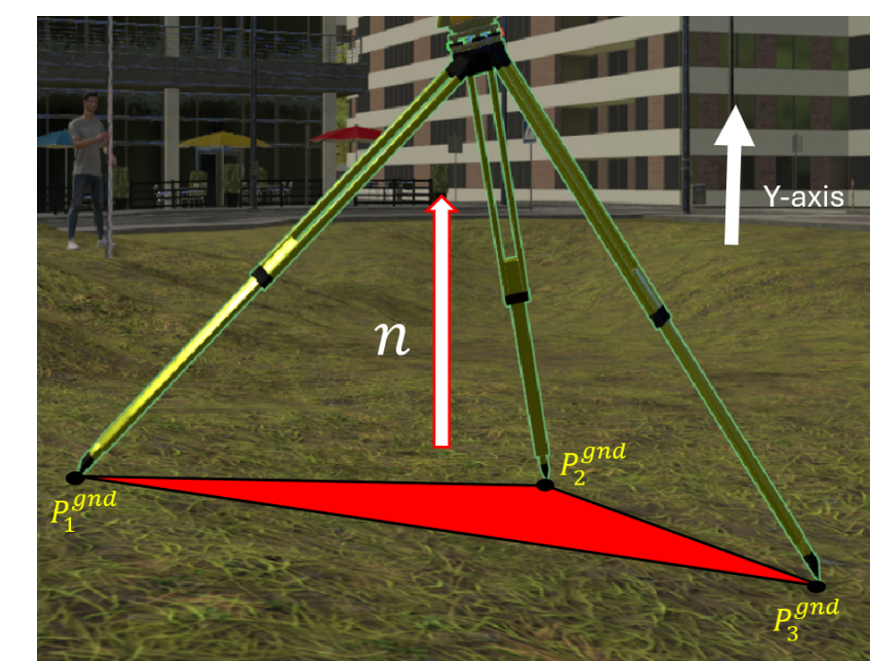 Vrise: A virtual reality platfrom for immersive and interactive surveying educationDaniel Udekwe , Dimitrios Bolkas , Eren Erman Ozguven , and 2 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2507.22810, 2025
Vrise: A virtual reality platfrom for immersive and interactive surveying educationDaniel Udekwe , Dimitrios Bolkas , Eren Erman Ozguven , and 2 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2507.22810, 2025Surveying is a core component of civil engineering education, requiring students to engage in hands-on spatial measurement, instrumentation handling, and field-based decision-making. However, traditional instruction often poses logistical and cognitive challenges that can hinder accessibility and student engagement. While virtual laboratories have gained traction in engineering education, few are purposefully designed to support flexible, adaptive learning in surveying. To address this gap, we developed Virtual Reality for Immersive and Interactive Surveying Education (VRISE), an immersive virtual reality laboratory that replicates ground-based and aerial surveying tasks through customizable, accessible, and user-friendly modules. VRISE features interactive experiences such as differential leveling with a digital level equipment and waypoint-based drone navigation, enhanced by input smoothing, adaptive interfaces, and real-time feedback to accommodate diverse learning styles. Evaluation across multiple user sessions demonstrated consistent gains in measurement accuracy, task efficiency, and interaction quality, with a clear progression in skill development across the ground-based and aerial surveying modalities. By reducing cognitive load and physical demands, even in tasks requiring fine motor control and spatial reasoning, VRISE demonstrates the potential of immersive, repeatable digital environments to enhance surveying education, broaden participation, and strengthen core competencies in a safe and engaging setting.
@article{udekwe2025vrise, title = {Vrise: A virtual reality platfrom for immersive and interactive surveying education}, author = {Udekwe, Daniel and Bolkas, Dimitrios and Ozguven, Eren Erman and Moses, Ren and Guo, Qianwen}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2507.22810}, year = {2025}, dimensions = {true}, } -
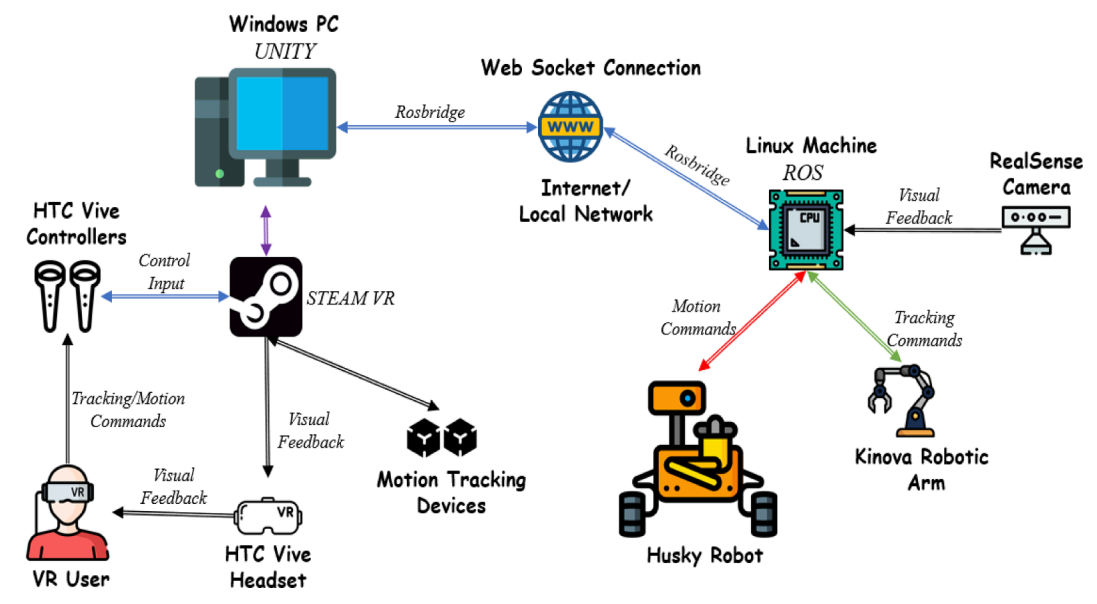 Human robot interaction for agricultural Tele-Operation, using virtual Reality: A feasibility studyDaniel Udekwe , and Hasan SeyyedhasaniComputers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2025
Human robot interaction for agricultural Tele-Operation, using virtual Reality: A feasibility studyDaniel Udekwe , and Hasan SeyyedhasaniComputers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2025With the increasing demand for efficient and sustainable agricultural practices, the automation of tasks such as crop inspection and harvesting has become a critical endeavor. However, the complex and dynamic nature of agricultural environments poses challenges for conventional methods that are fully autonomous or those relying on traditional interfaces. To address these challenges, we propose a solution that leverages the capabilities of Virtual Reality (VR) to provide operators with an intuitive and immersive control experience. This paper introduces a novel method for tele-operating a robotic system in agriculture using VR technology. By integrating a VR device with SteamVR and Unity 3D, users can control a mobile robotic module over a local network or the internet using VR hand controllers and a headset. In order to validates the system feasibility, we case studied two agricultural operations in lab settings: leaf inspection and crop harvesting. The results of this study were evaluated based on the cycle completion time (CCT) and the success rate of robot-plant interaction (RPI). For fruit harvesting, with a sample size (N) = 5, the mean CCT was approximately 18 s, with a standard deviation of nearly 5 s, indicating an improvement compared to existing autonomous systems in the literature. Additionally, in the leaf inspections, the mean CCT resulted in approximately 26 s with the standard deviation of nearly 6 s with the same sample size. The RPI success rate reached up to 90 % in the fruit harvesting practices. And in leaf inspection practices, this metric averaged two attempts per diseased leaf, 50 %, to grasp it and bring it to the operator’s attention. Through this study, the combination of consumer-grade VR technologies with a mobile robotic manipulation system highlights the system’s promise in improving remote agricultural tasks, especially in response to labor scarcity and improving farmworker efficiency.
@article{udekwe2025human, title = {Human robot interaction for agricultural Tele-Operation, using virtual Reality: A feasibility study}, author = {Udekwe, Daniel and Seyyedhasani, Hasan}, journal = {Computers and Electronics in Agriculture}, volume = {228}, pages = {109702}, year = {2025}, publisher = {Elsevier}, dimensions = {true}, } -
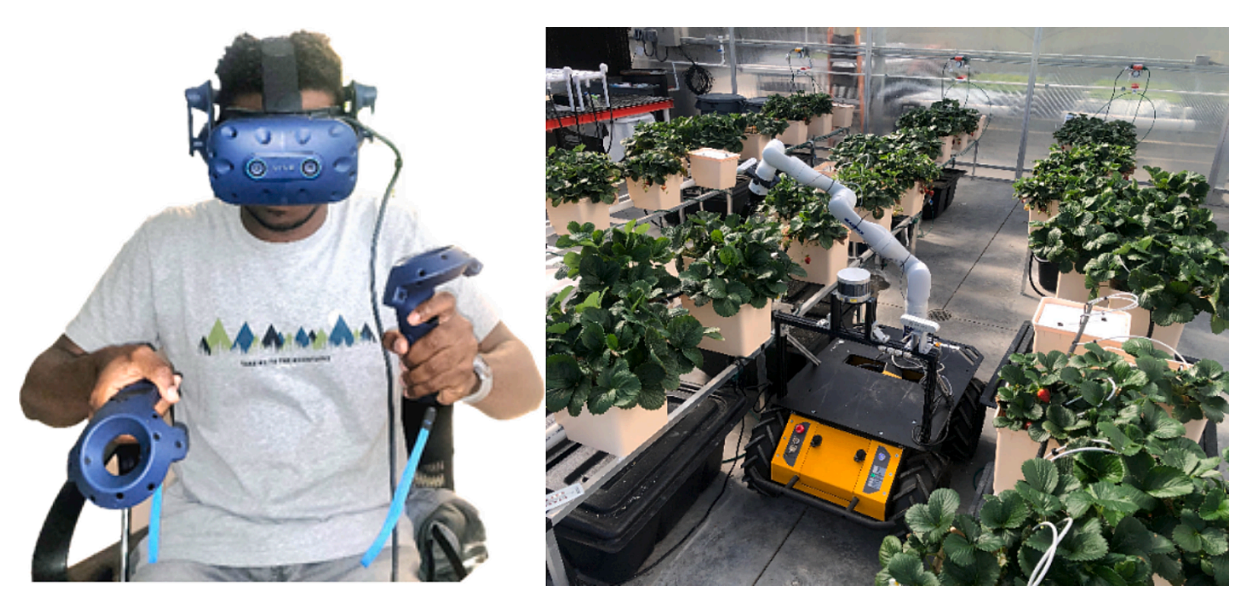 Virtual Reality-Enabled remote Human-Robot interaction for strawberry cultivation in greenhousesDaniel Udekwe , and Hasan SeyyedhasaniComputers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2025
Virtual Reality-Enabled remote Human-Robot interaction for strawberry cultivation in greenhousesDaniel Udekwe , and Hasan SeyyedhasaniComputers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2025This paper investigates the application of a VR-controlled robotic system for yield monitoring in strawberry farming within a greenhouse environment. The study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of the system in identifying and counting ripe strawberries, categorized by size (small and large) and variety (Seascape and Albion), and compares with the obtained results by an onsite human expert. We designed experiments, in a controlled environment agriculture center, and conducted in two trials. The yield monitoring performance of the developed robotic system was evaluated based on two primary metrics of cycle completion times and fruit detection accuracy, 32 strawberry plants which grew 336 ripe fruits. In the first experiment, the system achieved detection rates of 63 % for small strawberries and 72 % for large strawberries, with cycle completion times ranging from 12.5 to 16 s. In the second experiment, improvements were observed, with detection rates increasing to 74 % for both sizes and cycle completion times reduced to between 11.9 and 15.7 s. The developed robotic system demonstrated high accuracy and efficiency, particularly with larger strawberries. However, some limitations were identified, including challenges related to occlusion. These findings suggest that while the VR-controlled robotic system has the potential to complement and even surpass traditional yield monitoring methods managed by human experts, further refinements are necessary. Future research should focus on optimizing the system’s performance and adapting the system to broader applications in agriculture.
@article{udekwe2025virtual, title = {Virtual Reality-Enabled remote Human-Robot interaction for strawberry cultivation in greenhouses}, author = {Udekwe, Daniel and Seyyedhasani, Hasan}, journal = {Computers and Electronics in Agriculture}, volume = {237}, pages = {110567}, year = {2025}, publisher = {Elsevier}, dimensions = {true}, }
2024
-
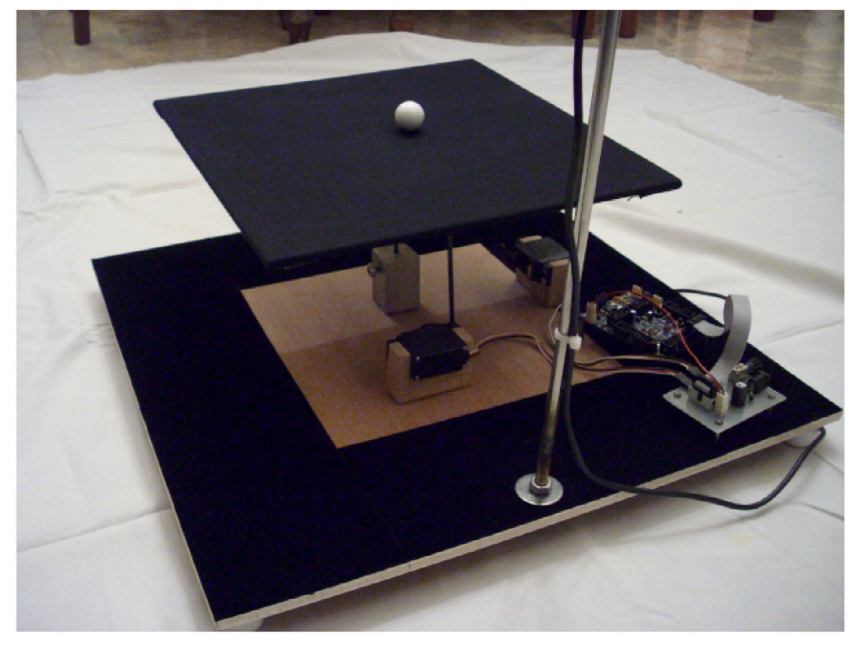 Comparing actor-critic deep reinforcement learning controllers for enhanced performance on a ball-and-plate systemDaniel Udekwe , Ore-ofe Ajayi , Osichinaka Ubadike , and 2 more authorsExpert systems with applications, 2024
Comparing actor-critic deep reinforcement learning controllers for enhanced performance on a ball-and-plate systemDaniel Udekwe , Ore-ofe Ajayi , Osichinaka Ubadike , and 2 more authorsExpert systems with applications, 2024The optimization of controller parameters remains an ongoing challenge in the field of control system applications. This study introduces a novel approach involving the creation of custom actor-critic deep reinforcement learning (DRL) based PID controllers. These controllers are designed with the goal of achieving adaptive tuning, precise trajectory tracking, and stability in a ball-and-plate system. To achieve this objective, multiple actor-critic reinforcement learning agents were developed using different learning algorithms: Soft actor critic (SAC), deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG), and twin delayed deep deterministic policy gradient (TD3). These agents incorporate multilayer-perceptron (MLP) policy learning algorithms in both the actor and critic network architectures, employing non-linear activation functions. This enables them to fine-tune PID control parameters within an infinite search space. Additionally, a custom reward function derived from the system’s environment was integrated into the learning process. The performance of the proposed methods was compared against a benchmark method, specifically, an existing deep reinforcement learning controllers reported in the literature. The evaluation of these controllers and other approaches was based on error metrics and time response analysis. Results demonstrate that the proposed controller denoted as SAC-PID(5) excelled in trajectory tracking and outperformed other methods. It exhibited minimal predictive errors and the shortest time responses in the majority of experiments. This highlights the significance of designing a customized SAC agents with appropriate network architecture, which positively impacts the learning process for intelligent tuning of controllers for classical control systems.
@article{udekwe2024comparing, title = {Comparing actor-critic deep reinforcement learning controllers for enhanced performance on a ball-and-plate system}, author = {Udekwe, Daniel and Ajayi, Ore-ofe and Ubadike, Osichinaka and Ter, Kumater and Okafor, Emmanuel}, journal = {Expert systems with applications}, volume = {245}, pages = {123055}, year = {2024}, publisher = {Elsevier}, dimensions = {true}, }
2021
-
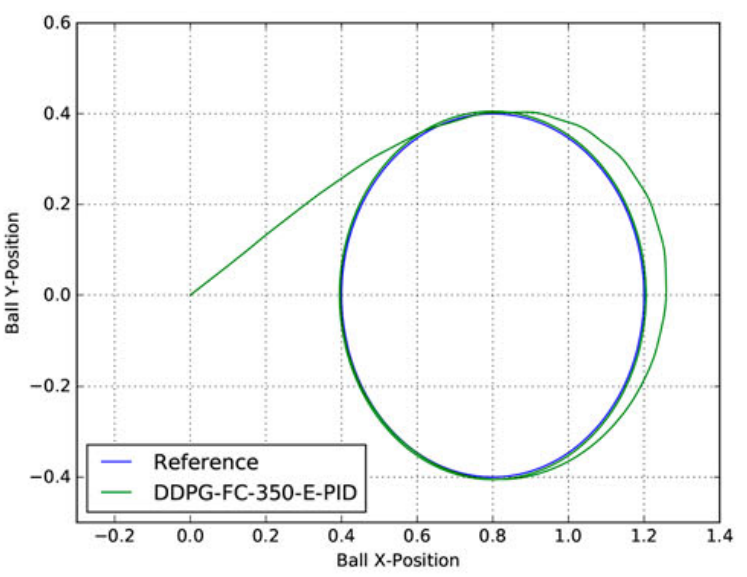 Heuristic and deep reinforcement learning-based PID control of trajectory tracking in a ball-and-plate systemEmmanuel Okafor , Daniel Udekwe , Yusuf Ibrahim , and 2 more authorsJournal of Information and Telecommunication, 2021
Heuristic and deep reinforcement learning-based PID control of trajectory tracking in a ball-and-plate systemEmmanuel Okafor , Daniel Udekwe , Yusuf Ibrahim , and 2 more authorsJournal of Information and Telecommunication, 2021The manual tuning of controller parameters, for example, tuning proportional integral derivative (PID) gains often relies on tedious human engineering. To curb the aforementioned problem, we propose an artificial intelligence-based deep reinforcement learning (RL) PID controller (three variants) compared with genetic algorithm-based PID (GA-PID) and classical PID; a total of five controllers were simulated for controlling and trajectory tracking of the ball dynamics in a linearized ball-and-plate (𝐵&𝑃) system. For the experiments, we trained novel variants of deep RL-PID built from a customized deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG) agent (by modifying the neural network architecture), resulting in two new RL agents (DDPG-FC-350-R-PID & DDPG-FC-350-E-PID). Each of the agents interacts with the environment through a policy and a learning algorithm to produce a set of actions (optimal PID gains). Additionally, we evaluated the five controllers to assess which method provides the best performance metrics in the context of the minimum index in predictive errors, steady-state-error, peak overshoot, and time-responses. The results show that our proposed architecture (DDPG-FC-350-E-PID) yielded the best performance and surpasses all other approaches on most of the evaluation metric indices. Furthermore, an appropriate training of an artificial intelligence-based controller can aid to obtain the best path tracking.
@article{okafor2021heuristic, title = {Heuristic and deep reinforcement learning-based PID control of trajectory tracking in a ball-and-plate system}, author = {Okafor, Emmanuel and Udekwe, Daniel and Ibrahim, Yusuf and Bashir Mu'azu, Muhammed and Okafor, Ekene Gabriel}, journal = {Journal of Information and Telecommunication}, volume = {5}, number = {2}, pages = {179--196}, year = {2021}, publisher = {Taylor \& Francis}, dimensions = {true}, }